The construction and building materials industries are shifting towards sustainable practices, with ceramsite sand emerging as a key innovation. The blog explores its advantages, production process, and wide applications.
What is ceramsite sand?
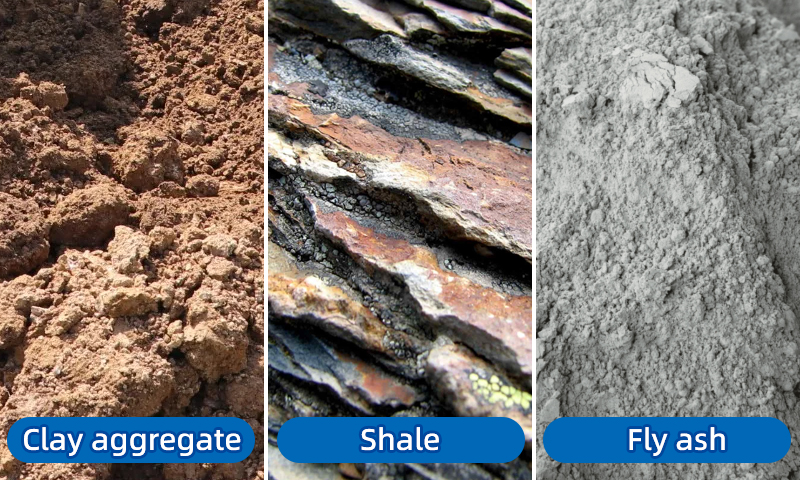
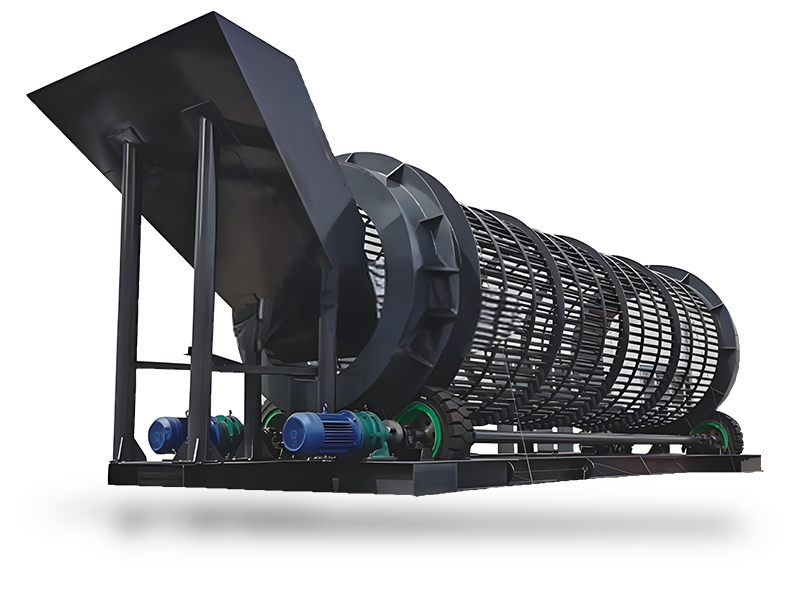
Ceramic sand is also known as the ceramic sand. It is a porous lightweight expanded clay aggregate made by sintering clay, shale, or other similar materials at high temperatures in a rotary kiln.
There are many raw materials, so the color of the fired ceramsite sand is mostly dark red, and reddish white, and some special varieties are grayish-yellow, grayish black, grayish white, cyan, etc.
Ceramic sand is mostly fine particles less than 5 mm. The main varieties are clay ceramsite sand, shale ceramsite sand, and fly ash ceramsite sand.
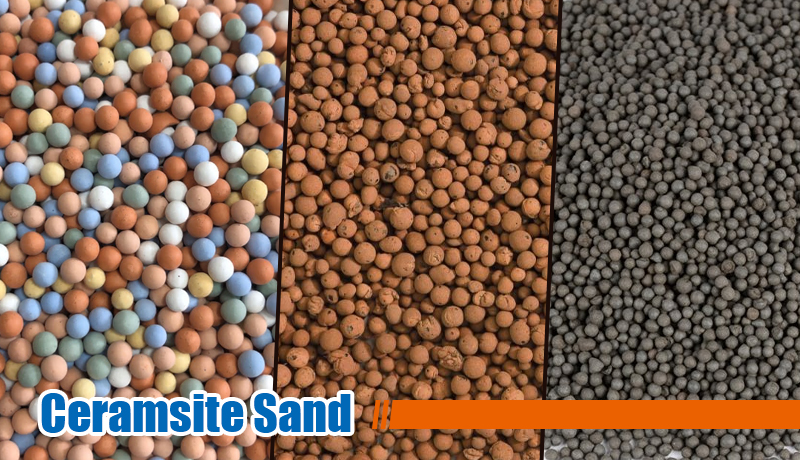

Due to its excellent physical and chemical properties, ceramsite sand has become an ideal choice for various construction applications. It is increasingly used in concrete production, lightweight bricks and soil improvement.
Compared with other normal construction materials, what are the advantages of ceramsite sand?
- Lightweight: Ceramsite sand is significantly lighter than traditional aggregates, reducing the overall weight of structures and contributing to lower transportation costs. Its lightweight nature makes it ideal for high-rise buildings and bridge construction.
- High strength: Despite its low density, ceramsite sand boasts high compressive strength. This property ensures that structures built with ceramsite sand can withstand heavy loads, making it a reliable choice for various construction projects.
- Thermal insulation: Ceramsite sand exhibits excellent thermal insulation properties, helping to regulate indoor temperatures and reduce energy consumption in buildings. This characteristic contributes to sustainable building practices and enhances occupant comfort.
- Environmental benefits: The production of ceramsite sand utilizes natural materials and can be made from industrial waste, contributing to waste reduction and environmental sustainability. By replacing traditional aggregates with ceramsite sand, the construction industry can minimize its carbon footprint.
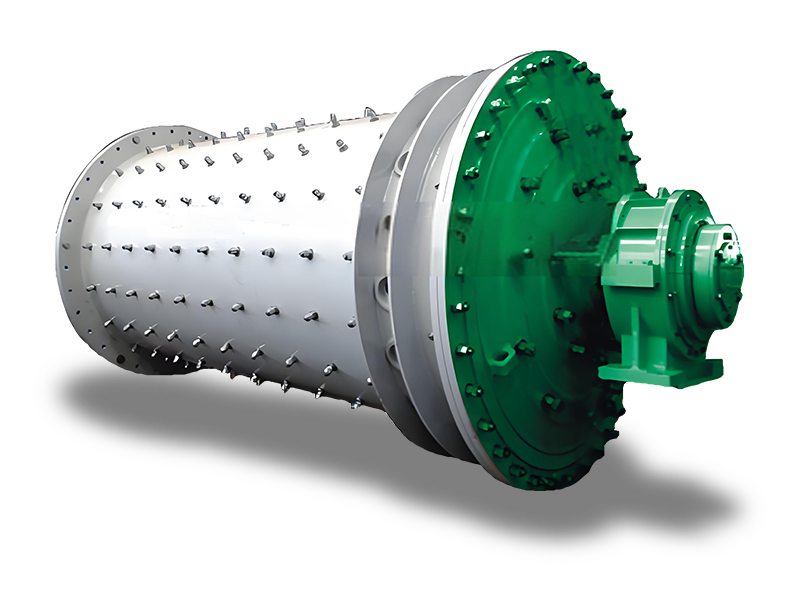
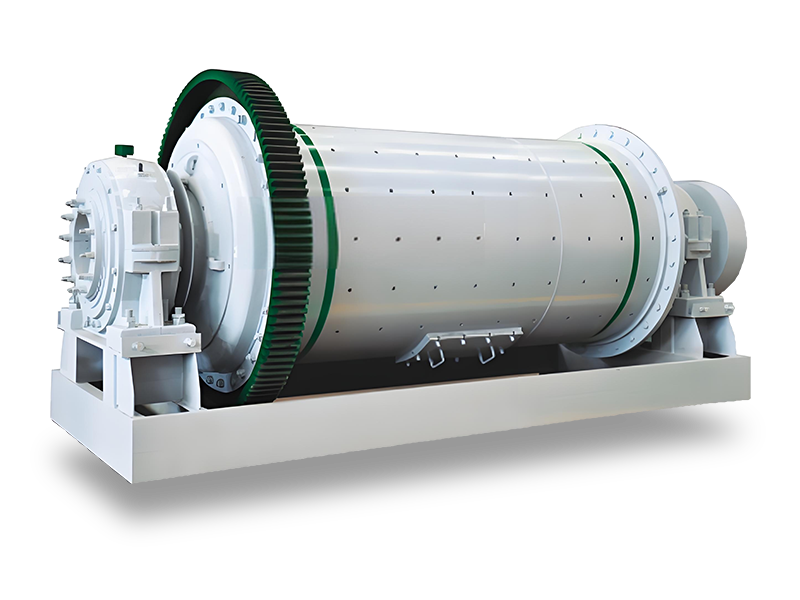
Producing ceramsite sand, a lightweight aggregate commonly used in construction and other applications, involves several steps. Here’s a concise guide to help you through the process:
1. Raw Material Selection
- Clay: The primary raw material. Select clay with good plasticity and low shrinkage.
- Additives: Sometimes, other materials like shale or slate are added to enhance properties.
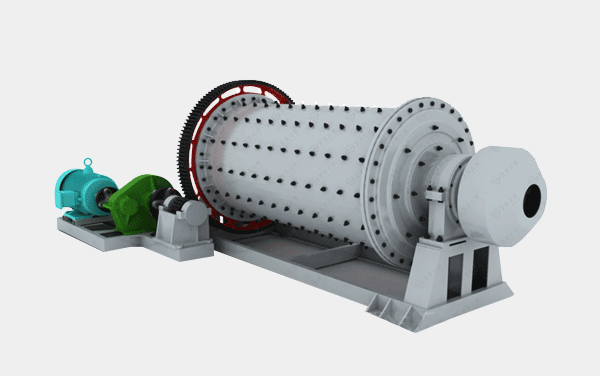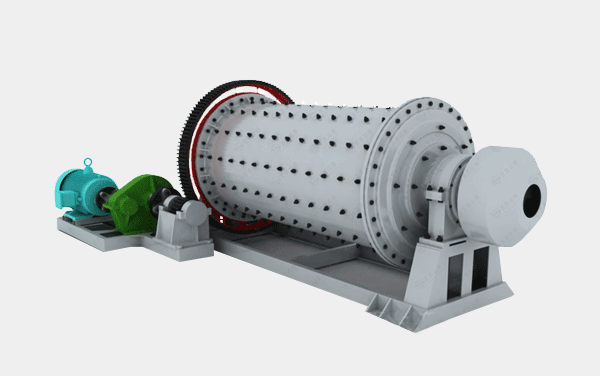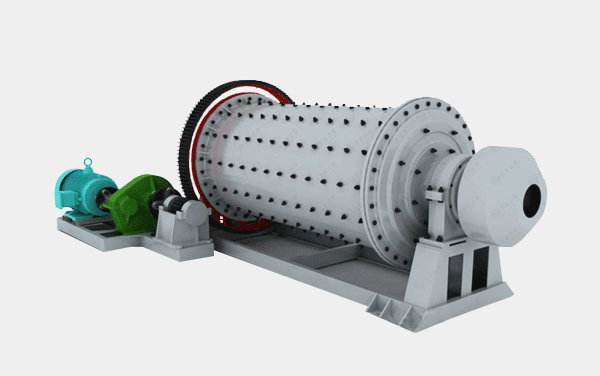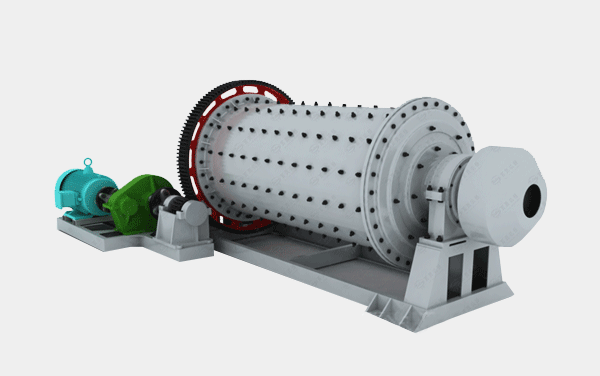
2. Crushing and Grinding
- Crushing: Break down large lumps of clay into smaller pieces to facilitate processing.
- Grinding: Mill the crushed clay to a fine powder to ensure uniformity.
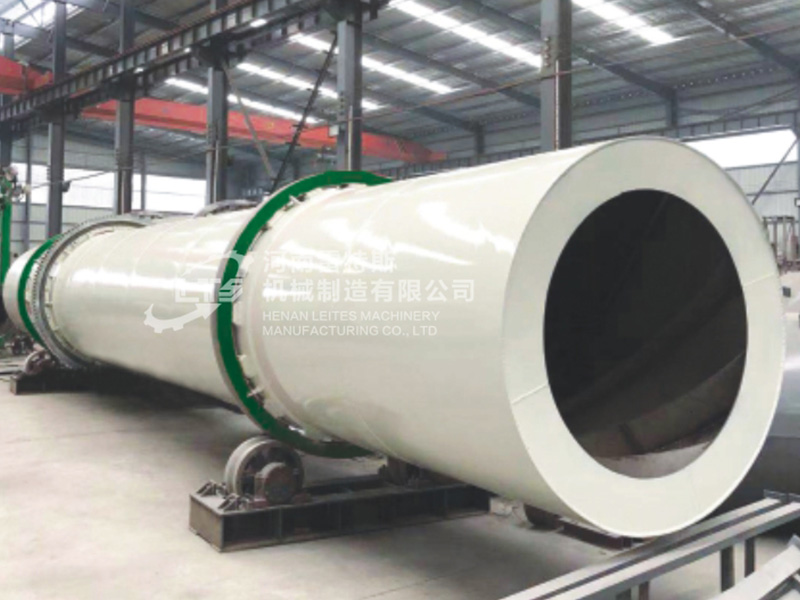
3. Pelletizing
- Mixing: Combine the ground clay with water and any additives to create a homogeneous mixture.
- Pelletizing: Form the mixture into small pellets. This can be done using a pellet mill or by hand-rolling.
4. Drying
- Air Drying: Allow the pellets to air dry until they reach a moisture content suitable for firing.
- Mechanical Drying: Use a drying machine if quicker results are needed.

5. Firing
- Kiln Preparation: Place the dried pellets in a kiln.
- Firing Process: Heat the pellets to temperatures between 1000°C to 1200°C (1832°F to 2192°F). This process vitrifies the clay, causing it to expand and form a lightweight aggregate.
6. Cooling
- Controlled Cooling: Gradually cool the fired ceramsite to avoid cracking. This step is crucial to maintain the integrity of the aggregate.
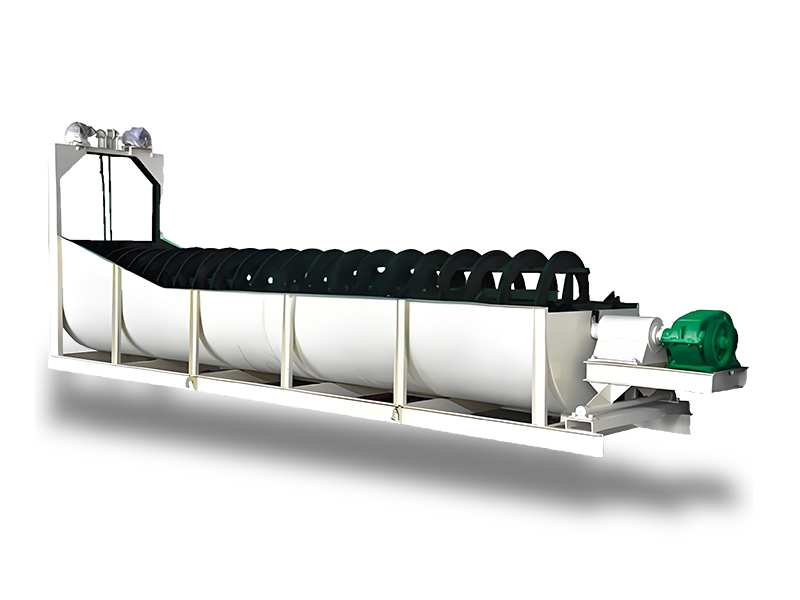
7. Screening and Quality Control
- Screening: Sift the cooled ceramsite to separate it into various size fractions.
- Quality Testing: Conduct tests to ensure the ceramsite meets the required specifications for strength, density, and durability.
8. Packaging and Storage
- Packaging: Store the ceramsite in appropriate containers or bags to protect it from moisture.
- Storage: Keep in a dry, cool environment until ready for use.
Applications
- Lightweight concrete
- Insulation materials
- Drainage systems
- Soil amendment in agriculture
Considerations
- Environmental Impact: Ensure compliance with environmental regulations regarding emissions during firing.
- Safety Measures: Follow safety protocols during handling and processing materials.
























 +8615713843888
+8615713843888
 +8615713843888
+8615713843888