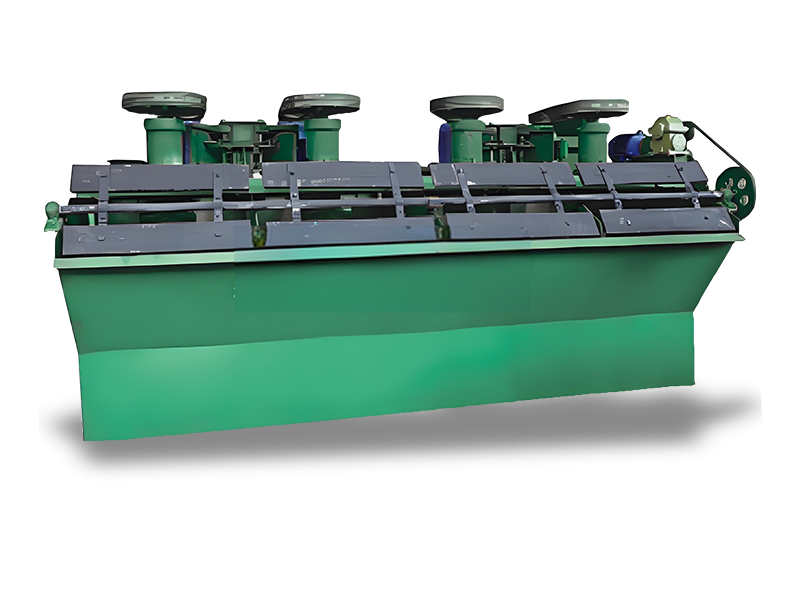
Usage: The mining flotation machine is widely used for rough selection, selection, and reverse flotation operations of non-ferrous metals such as copper, lead, zinc, nickel, and molybdenum, as well as black metals and non gold minerals.
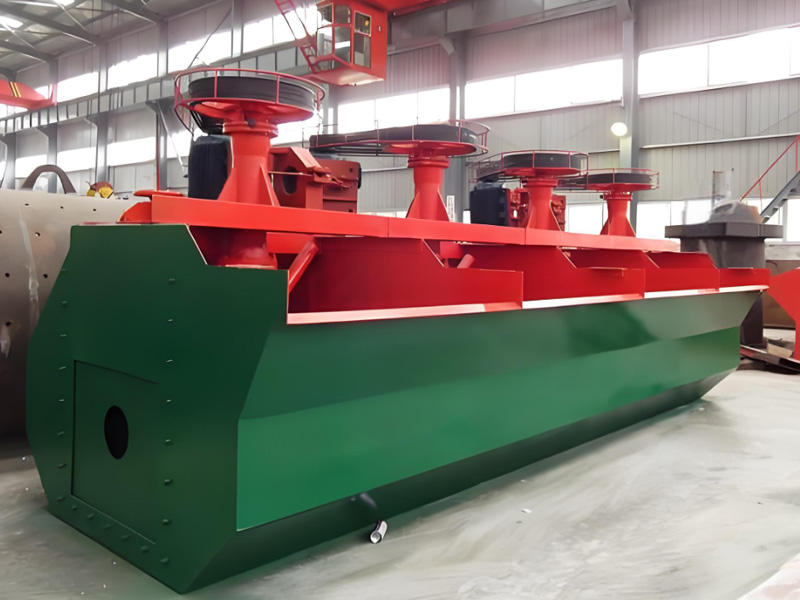

Key Features
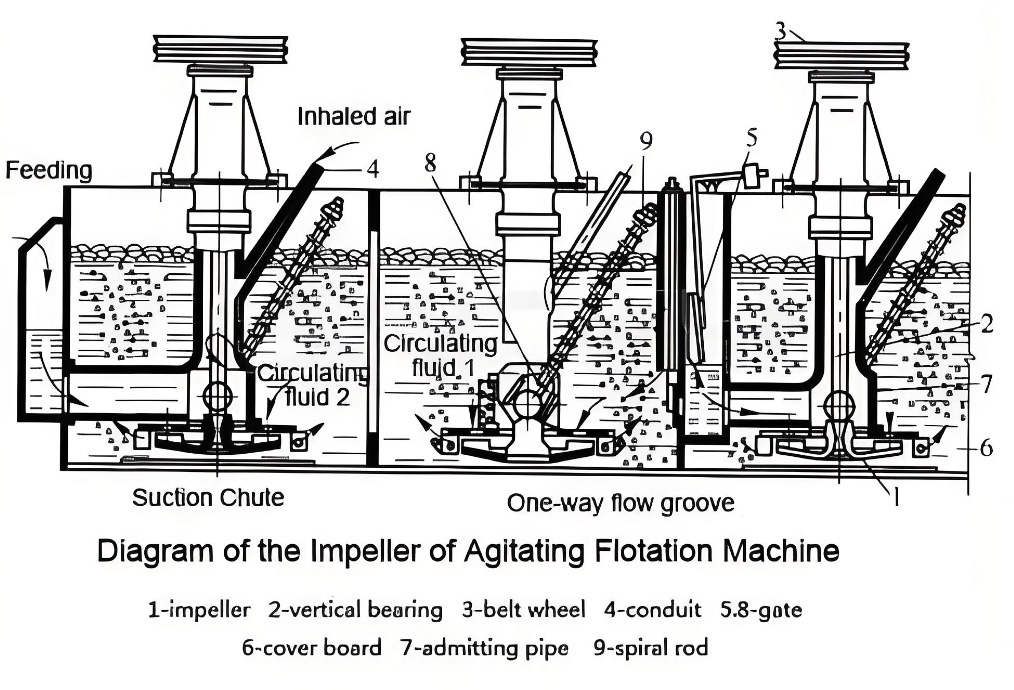
- Mechanical Design: Flotation machines come in various designs, including mechanical and column flotation types. They typically consist of a tank, impeller, and a system for introducing air.
- Air Supply System: These machines are equipped with a mechanism to introduce air bubbles into the slurry, which is essential for the flotation process.
- Adjustable Settings: Many flotation machines allow for adjustments in rotor speed, aeration rate, and pulp density, enabling optimization for specific ore types.
Working Principle
- Preparation of Slurry: The ore is crushed and ground to liberate the valuable minerals. This ground material is then mixed with water to form a slurry.
- Addition of Reagents: Collectors, frothers, and modifiers are added to the slurry to enhance the hydrophobic properties of the target minerals and stabilize the froth.
- Air Injection: Air is introduced into the slurry through the impeller. The agitator creates turbulence, allowing the air bubbles to interact with the minerals.
- Bubble Attachment: Hydrophobic (water-repelling) minerals attach to the air bubbles and rise to the surface, forming a froth layer.
- Froth Collection: The froth containing the concentrated minerals is collected from the surface, while the non-floatable materials sink to the bottom and are removed.
Applications
- Mineral Processing: Widely used for the separation of non-ferrous metals (like copper, lead, and zinc), precious metals (like gold and silver), and industrial minerals (like phosphate).
- Wastewater Treatment: Flotation machines can also be used to remove suspended solids from wastewater.

Benefits
- High Recovery Rates: Flotation machines can achieve high recovery rates for valuable minerals, improving the efficiency of the separation process.
- Versatility: They can be used for various ore types and different mineral recovery processes.
- Cost-Effectiveness: The flotation process often results in a higher grade of concentrate, which can reduce downstream processing costs.
Maintenance Tips
- Regularly check and maintain the air supply system to ensure efficient operation.
- Monitor reagent levels and adjust as necessary for optimal performance.
- Inspect and clean the impeller and other mechanical parts to prevent wear and tear.
























 +8615713843888
+8615713843888
 +8615713843888
+8615713843888